

Biomass Gasification
Overview – Biomass Gasification
Biomass gasification is an alternative option of thermal biomass utilisation for the production of heat and power based on biomass or for the production of synthesis gas. Within the last 20 years several different gasification technologies have been developed and demonstration plants have been realised. Based on the experience from these demonstration plants the gasification technologies have been further developed. Thus, some gasification technologies have now entered the market or are close to market introduction.
In addition to the evaluation and process implementation of existing gasification technologies, BIOS is intensively working on the development of new processes based on a fuel-flexible fixed-bed countercurrent gasification technology which has been invented by BIOS.
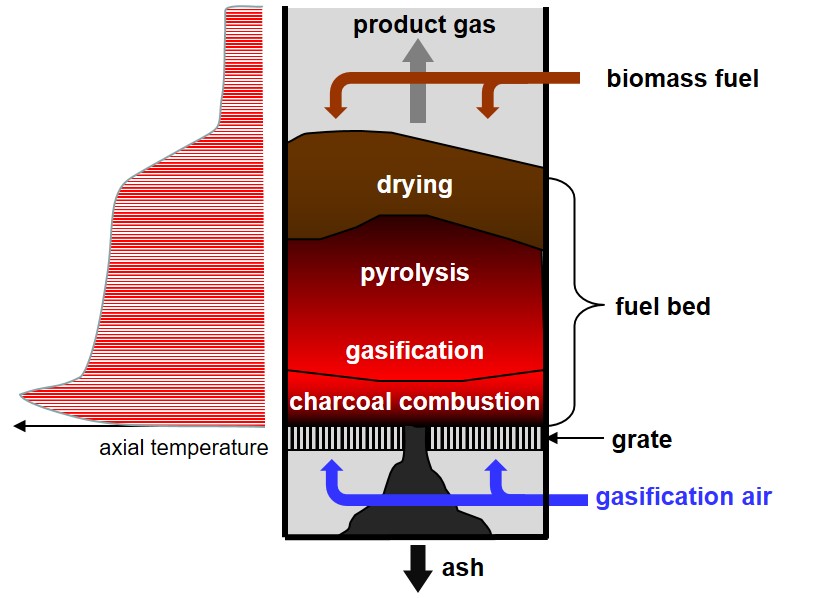
Figure 1: Updraft gasification concept – schematic drawing
Gasification technology
Gasification plants consist of several process steps, which are shown in Figure 2. The solid biomass fuel delivered needs to be adjusted (fuel conditioning and handling) to the fuel characteristics (particle size, water content) required for the gasification process. The conditioned fuel enters the gasification process, which produces raw product gas. The raw product gas needs to be cleaned in order to achieve the product gas quality needed for further utilisation. The cleaned product gas is used for the production of electric power, heat, liquid fuels or synthesis gas depending on the technology applied.
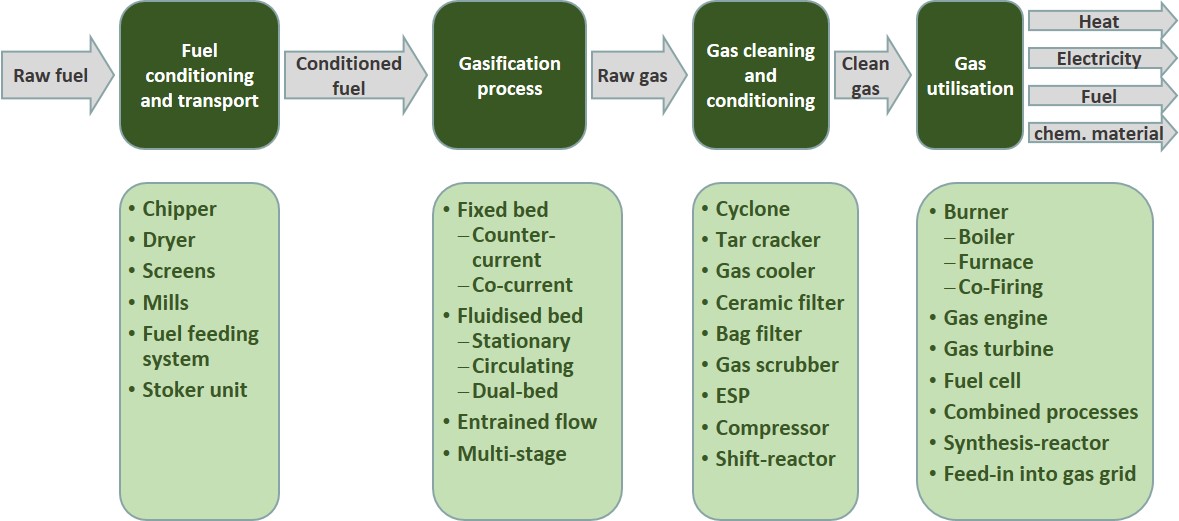
Figure 2: Basic process steps of a biomass gasification plant
Explanations: The dark green rectangles show the process steps while the arrows show the conversion stages of the fuel during the gasification process. The light green rectangles below show the different technological options for each process step.
During the thermo-chemical biomass gasification process solid biomass is cracked by thermal energy and a gasification agent and converted into a product gas. The product gas is cleaned and used for the production of heat and power, e.g. by gas engines (biomass CHP) or converted into a liquid biomass fuel or synthesis gas.
The main advantage of the biomass gasification technology is the high electric efficiency due to the power production with gas engines or fuel cells. Even more than 40% electric efficiency (related to the net calorific value of the product gas) are achievable with fuels cells (solid oxide fuel cells – SOFC), a technology which is presently under development at BIOS within R&D projects. Furthermore, alternative applications of the product gas such as production of liquid fuels or synthesis gas are possible.
The high temperature waste heat of the gasification process and the gas engine resp. SOFC system can be used in an ORC unit in order to produce additional electric power and further increase the electric plant efficiency.
Low temperature waste heat can be used for space and process heat supply as well as for biomass fuel drying. An efficient heat utilisation is necessary in order to achieve high overall plant efficiencies and to improve the economy.
Procedure for the selection and evaluation of biomass gasification technologies
The following procedure is recommended for the evaluation of the feasibility of biomass gasification technologies:
- Technological evaluation and comparison of different biomass gasification systems – important, since many systems are still under development or demonstration and no long-term experiences are available
- Economic evaluation of the gasification technologies compared to a reference system (e.g. biomass CHP plant based on combustion) – important, since a high electric efficiency does not necessarily mean a better economic performance (investment and operation costs as well as availability have to be considered as well)
- Evaluation of already available reference plants for a particular gasification technology – important, in order to obtain information regarding reliability and availability
- Verification of the emissions (exhaust gas, waste water, ash) of gasification plants compared to expected emission limits and guiding values – important since an ecological operation based on economically meaningful side constraints is required
- Overall evaluation of the systems based on the results of topics 1) to 4)
BIOS BIOENERGIESYSTEME GmbH performs this evaluation procedure based on appropriate expertise and in a neutral way.
Working field of BIOS BIOENERGIESYSTEME GmbH
- Development, comparison as well as technical, economic and ecological evaluation of different biomass gasification technologies as a basis for the selection of an adequate technology
- Planning of add-on power production systems for efficient waste heat utilisation (e.g. based on an ORC process)
- Feasibility studies including technological comparisons and screening for funding
- Preparation of permit applications as well as applications for funding
- Detailed design, request for proposals (RFP)
- Supervision of plant construction and commissioning
- Plant monitoring, process and performance optimisation
- R&D projects regarding the development of new and innovative biomass CHP technologies based on biomass updraft gasification with gas utilisation in gas engines, fuel cells and for the production of green chemicals
